java的会话管理:Cookie和Session
1.什么是会话
此处的是指客户端(浏览器)和服务端之间的数据传输。例如用户登录,购物车等
会话管理就是管理浏览器客户端和服务端之间会话过程产生的会话数据常用的会话技术 之前学会了域对象的作用,所以在会话管理的时候也可以使用域对象的概念来找到解决方法。 常用的解决方法主要有两种: 数据保存在客户端的Cookie技术 数据保存在服务端的Session技术2.Cookie技术
2.1.什么是Cookie
Cookie是客户端技术,程序把每个用户的数据以cookie的形式写给用户各自的浏览器,当用户使用浏览器再去访问服务器中的web资源时,就会带着各自的数据去。这样,web资源处理的就是各自用户自己的数据了
特点是会话数据保存在浏览器客户端2.2.Cookie技术核心API
Cookie类:用于存储会话数据。常用方法如下:
1.构造Cookie对象Cookie(java.lang.String name, java.lang.String value)
2.设置cookie
void setPath(java.lang.String uri) :设置cookie的有效访问路径
void setMaxAge(int expiry) : 设置cookie的有效时间 void setValue(java.lang.String newValue) :设置cookie的值
3.发送cookie到浏览器端保存
void response.addCookie(Cookie cookie) : 发送cookie
4.服务器端接收cookie
Cookie[] request.getCookies() : 接收cookie
代码示例:
/** * 测试Cookie的方法 */@WebServlet(name = "CookieDemo")public class CookieDemo extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { //1.创建Cookie对象 Cookie cookie = new Cookie("name","eric"); //2.设置Cookie参数 //2.1.设置Cookie的有效路径 cookie.setPath("/hello");//默认就是web项目的地址 //2.2.设置Cookie的有效时间 cookie.setMaxAge(20);//该cookie只存活20秒,从最后不调该cookie开始计算 cookie.setMaxAge(-1);//该cookie保存在浏览器内存中,关闭浏览器则销毁该cookie cookie.setMaxAge(0);//删除根该cookie同名的cookie //3.把数据发送到浏览器 response.addCookie(cookie); //4.服务端接收来自浏览器的cookie //方法1:// String name = request.getHeader("cookie");// System.out.println(name); //方法2: Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); //注意:判断null,否则空指针 if(cookies!=null){ //遍历 for(Cookie c:cookies){ String name = c.getName(); String value = c.getValue(); System.out.println(name+"="+value); } }else{ System.out.println("没有接收cookie数据"); } }} 2.3.Cookie原理
1.服务器创建Cookie对象,把会话数据存储到Cookie对象中
new Cookie("name","value");
2.服务器发送cookie信息到浏览器
response.addCookie(cookie);
其实是隐藏发送了一个set-cookie名称的响应头
3.浏览器得到服务器发送的cookie,然后保存在浏览器端
4.浏览器在下次访问服务器时,会带着cookie信息包含在http的请求头里
5.服务器接收到浏览器带来的cookie信息
request.getCookies();
2.4.Cookie的细节
1.void setPath(java.lang.String uri):设置Cookie的有效访问路径,有效访问路径指的事Cookie的有效路径保存在哪里,那么浏览器在有效路径下访问服务器的时就会带着Cookie信息,否则不带Cookie信息,默认是在当时钱web项目的路径下
void setMaxAge(int expiry):设置Cookie的有效时间 expiry可以是正整数,负整数,和零 正整数:表示Cookie数据保存浏览器的缓存到硬盘中,数值表示保存的时间 负整数:表示Cookie数据保存到浏览器的内存中,浏览器关闭Cookie就丢失了 零:表示删除同名的Cookie数据 3.Cookie数据类型只能保存非中文字符串类型的。可以保存多个Cookie,但是浏览器一般只允许存放300个Cookie,每个站点最多存放20个Cookie,每个Cookie的大小限制为4KB。 2.5.Cookie案例:显示用户上次访问的时间
功能实现逻辑:
将时间保存在Cookie中,每次访问从Cookie里面调用 第一次访问: 1.获取当前时间,显示到浏览器中 2.创建Cookie对象,时间作为cookie值,名为:lastTime 3.把cookie发送到浏览器保存 第N次访问: 1.获取cookie的数据,取出名为lastTime的cookie 2.得到cookie的值(上次访问时间) 3.显示上次访问时间到浏览器中 4.更新名为lastTime的cookie。值设置为当前时间 5.把更新后的cookie发送给浏览器保存代码实现:
/** * 案例-用户上次访问的时间 */@WebServlet("/last")public class HistServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); //获取当前时间 SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"); String curTime = format.format(new Date()); //取得cookie Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); String lastTime = null; //第n次访问 if(cookies!=null){ for (Cookie cookie : cookies) { if(cookie.getName().equals("lastTime")){ //有lastTime的cookie,已经是第n次访问 lastTime = cookie.getValue();//上次访问的时间 //第n次访问 //1.把上次显示时间显示到浏览器 response.getWriter().write("欢迎回来,你上次访问的时间为:"+lastTime+",当前时间为:"+curTime); //2.更新cookie cookie.setValue(curTime); cookie.setMaxAge(1*30*24*60*60); //3.把更新后的cookie发送到浏览器 response.addCookie(cookie); break; } } } /** * 第一次访问(没有cookie 或 有cookie,但没有名为lastTime的cookie) */ if(cookies==null || lastTime==null){ //1.显示当前时间到浏览器 response.getWriter().write("你是首次访问本网站,当前时间为:"+curTime); //2.创建Cookie对象 Cookie cookie = new Cookie("lastTime",curTime); cookie.setMaxAge(1*30*24*60*60);//保存一个月 //3.把cookie发送到浏览器保存 response.addCookie(cookie); } }} 2.6.Cookie案例:查看用户浏览过的商品
逻辑图
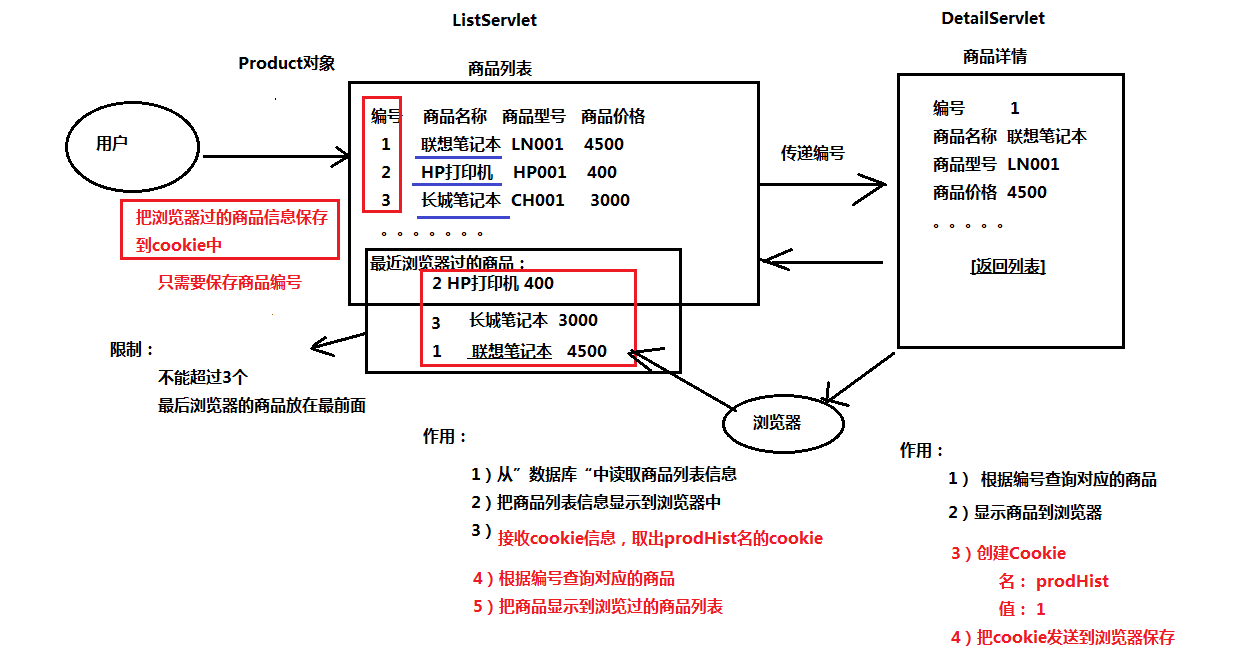
这个项目的代码较多,按照功能的不同放在不同的包里面
公司域名的倒写+项目名字+功能名字 cenyu.hist.entity 存放实体对象 cenyu.hist.dao Data Access Object 数据访问对象,主要存放实体对象的一些方法(CRUD-create,read,update,delete) cenyu.hist.servlet 存放servlet程序 cenyu.hist.ytil 存放工具类 cenyu.hist.test 存放测试类 等等 写的顺序:实体对象-->DAO类-->Servlet程序代码:暂无
3.Session技术
3.1.什么是Session
Session是服务器端技术,利用这个技术,服务器在运行时可以为每一个用户的数据创建一个其独享的Session对象,由于Session为用户浏览器独享,所以当用户在访问服务器的web资源时,可以把各自的数据放在各自的Session中,当用户再去访问服务器中的其他的web资源的时候,其他的web资源再从用户各自的Session中取出数据为用户服务
3.2.Session的核心技术
Session的类是HttpSession类:用于保存会话数据
1.创建或得到session对象HttpSession getSession() 直接创建一个Session对象HttpSession getSession(boolean create) 接收布尔值,设置为true时,在没有找到匹配Session编号的对象时新建一个Sessionu对象。如果设置false,则当找不到匹配的Session时,返回null,建议不要用2.设置session对象void setMaxInactiveInterval(int interval) : 设置session的有效时间java.lang.String getId() : 得到session编号void invalidate() : 销毁session对象 Session对象的方法: 1.setMaxInactiveInterval方法默认30分钟自动回收Session对象 2.使用setMaxInactiveInterval方法修改销毁时间 3.在web.xml文件中全局修改Session默认回收时间 1
4.通过invalidate方法,手动销毁Session对象
3.保存会话数据到session对象
void setAttribute(java.lang.String name, java.lang.Object value) : 保存数据 java.lang.Object getAttribute(java.lang.String name) : 获取数据 void removeAttribute(java.lang.String name) : 清除数据4.如何避免浏览器的JSESSIONID的cookie随着浏览器关闭而丢失的问题:
解决方法是手动发送一个硬盘保护的cookie给浏览器 代码见案例:/** * 测试Session的方法 */@WebServlet(name = "SessionServletDemo")public class SessionServletDemo extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { //1.创建Session对象 HttpSession session = request.getSession(); //2.保存会话数据 session.setAttribute("name","eric"); //3.取出会话数据 String name = (String)session.getAttribute("name"); System.out.println(name); //4. //拿到Session的id System.out.println(session.getId()); //修改Session有效时间 session.setMaxInactiveInterval(20); //销毁session if (session!=null){ session.invalidate(); } //手动发送一个硬盘保存的cookie给浏览器 Cookie c = new Cookie("JSESSION", session.getId()); c.setMaxAge(60*60); response.addCookie(c); }} 3.3.Session原理
代码解读:HttpSession session = request.getSession();
伪码分析执行过程 1.第一次访问创建Session对象,给Session对象分配一个唯一的ID,叫JSESSIONID。new HttpSession();
2.把JSESSIONID作为Cookie的值发送给浏览器保存
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("JSESSIONID", sessionID);
response.addCookie(cookie);
3.第二次访问的时候,浏览器带着JSESSIONID的cookie访问服务器
4.服务器得到JSESSIONID,在服务器的内存中搜索是否存放对应编号的session对象 5.如果找到对应编号的session对象,直接返回该对象 6.如果找不到对应编号session对象,创建新的session对象,继续走1的流程结论通过JSESSION的cookie值在服务器找session对象
3.4.Session案例:用户登录效果
需求:实现用户登录效果,如果登录成功显示:欢迎回来,×××。如果失败,显示登录失败
使用Session区分不同的用户来实现,整个代码实现分为三块,登录表单提交之后的处理逻辑,登录逻辑,登出逻辑: 默认登录界面。index.html登录页面
登录失败页面:fail.html
信息提示页面 亲, 你的用户名或密码输入有误!请重新输入! 返回登录页面
表单提交之后的主处理逻辑:IndexServlet.java
/** * 用户主页的逻辑 * */public class IndexServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter(); String html = ""; /** * 接收request域对象的数据 */ /* String loginName = (String)request.getAttribute("loginName"); */ /** * 二、在用户主页,判断session不为空且存在指定的属性才视为登录成功!才能访问资源。 * 从session域中获取会话数据 */ //1.得到session对象 HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); if(session==null){ //没有登录成功,跳转到登录页面 response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/login.html"); return; } //2.取出会话数据 String loginName = (String)session.getAttribute("loginName"); if(loginName==null){ //没有登录成功,跳转到登录页面 response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/login.html"); return; } html = "欢迎回来,"+loginName+",安全退出"; writer.write(html); } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); }} 登录处理逻辑:LoginServlet.java
/** * 处理登录的逻辑 * */public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //1.接收参数 String userName = request.getParameter("userName"); String userPwd = request.getParameter("userPwd"); //2.判断逻辑 if("eric".equals(userName) && "123456".equals(userPwd)){ //登录成功 /** * 分析: * context域对象:不合适,可能会覆盖数据。 * request域对象: 不合适,整个网站必须得使用转发技术来跳转页面 * session域对象:合适。 */ /* request.setAttribute("loginName", userName); //request.getRequestDispatcher("/IndexServlet").forward(request, response); response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/IndexServlet"); */ /** * 一、登录成功后,把用户数据保存session对象中 */ //1.创建session对象 HttpSession session = request.getSession(); //2.把数据保存到session域中 session.setAttribute("loginName", userName); //3.跳转到用户主页 response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/IndexServlet"); }else{ //登录失败 //请求重定向 response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/fail.html"); } } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); }} 退出处理逻辑:LogoutServlet.java
/** * 退出逻辑 * */public class LogoutServlet extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { /** * 三、安全退出: * 删除掉session对象中指定的loginName属性即可! */ //1.得到session对象 HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); if(session!=null){ //2.删除属性 session.removeAttribute("loginName"); } //2.回来登录页面 response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/login.html"); } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); }} 3.5.案例:Session实现通讯录
暂无